when some of the substance exists as ions, and the other part exists as the entire molecule.
eg. bromine water, when in a closed bottle, it seems that it is a static equilibrium, ie. some will evaporate into gas, and the rest will stay in solution, but in reality, a dynamic equilibrium is set up, where molecules are evaporating and being dissolved in solution at all times, and the gas/solution will always be the same concentration. it can be observed by the gas staying the same colour, not getting any darker.
if the pressure was increased on the gas, more molecules will be dissolved into solution, to counteract the pressure change.
also,
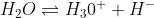
if any H- ions are added, it will change to H2O by using up some H3O+ ions to counteract the excess in H- ions.
also, with acids, strong acids completely ionise. weak acids exist in equilibrium, and therefore do not completely ionise.
i hope that makes sense, sorry if it doesn't.