This question can effectively be broken into two 'pieces'
Because the net acceleration is directly downwards at the peak of the curvature, the rollercoaster is effectively in uniform circular motion at this instant. Hence, we can use the formula for uniform circular motion:
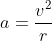
The acceleration is gravity (9.8), and the radius is 8 (given), so using the formula we can determine the velocity to be 8.85.
Because the rollercoaster has negligible speed initially and no friction, all of the kinetic energy comes from the change in height. This means that we just need to find the height from any fall ending in the same velocity, irrespective of the horizontal movement.
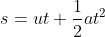
The initial velocity is zero, acceleration is 9.8, we don't yet know t and we need to find s.
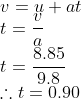
And hence we can use the equation from earlier
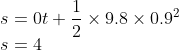
So the answer is A